Quartz plates are vital in various industries, providing unique properties that make them invaluable. Dr. Emily Chen, a leading expert in materials science, once remarked, "The precision and durability of a quartz plate are unmatched in modern technology." This statement highlights the significance of quartz plates in applications ranging from optics to electronics.
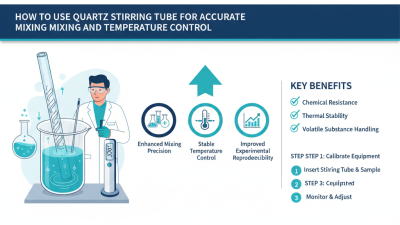
These plates offer exceptional thermal stability and chemical resistance. Many laboratories and manufacturing facilities depend on their reliability. However, usages may vary with specific requirements. Each application demands a careful assessment of qualities like thickness, purity, and surface finish. Such attention to detail ensures optimal performance and longevity, but it can also lead to oversight if not managed properly.
Despite their advantages, the industry faces challenges. High-quality quartz can be expensive and hard to source. Companies must balance cost with quality, sometimes leading to compromised choices. Reflecting on these challenges, it becomes clear that understanding the precise needs for quartz plates is crucial. A well-informed decision can make all the difference in achieving desired outcomes.

Quartz plates are essential components in various fields, especially in scientific and industrial applications. Made from pure quartz, these plates have unique properties. They are highly transparent to ultraviolet light and are resistant to chemical corrosion. This makes them ideal for use in laboratories and optical devices. Many researchers and engineers rely on quartz plates for precise measurements.
Understanding their role is crucial. Quartz plates are used in spectroscopy, where they help analyze light spectra. Their stability under temperature changes makes them suitable for thermal applications. However, not all quartz plates are the same. Some might contain impurities or defects that affect performance. Careful selection is necessary to avoid issues during experiments.
In many cases, proper handling of quartz plates is overlooked. They can be fragile and may require specific cleaning methods. A scratch can compromise their integrity. Some users might underestimate the importance of these details. This can lead to unexpected results or equipment damage. Observing best practices is vital to maintain their functionality.
Quartz plates are made from natural quartz crystal. This mineral is abundant and well-known for its durability. Composed mainly of silicon dioxide, quartz has a hardness of 7 on the Mohs scale. This makes it resistant to scratches and wear. The transparency of quartz allows for precise light transmission. Its unique properties make it suitable for various applications.
These plates are often used in optics and electronics. Their ability to withstand high temperatures is beneficial in laboratory settings. Quartz plates also possess excellent chemical resistance. However, they can be brittle, which sometimes results in unexpected breakage. Handling requires care to prevent chipping or cracking.
The manufacturing process of quartz plates influences their quality. Different purities may lead to varied performance outcomes. Some plates might not meet the ideal specifications for sensitive applications. Depending on the method used, inconsistencies may arise. It's important to consider these factors when choosing quartz plates for specific tasks.
Quartz plates have become essential in many industries. Their durability and resistance to thermal and chemical stress make them a favored choice. In the electronics sector, for instance, quartz plates are utilized in semiconductor fabrication. A report by the Semiconductor Industry Association noted that about 80% of semiconductor devices require high-quality quartz components.
In the optical field, quartz plates serve as substrates for various applications. They provide excellent transmittance of ultraviolet light, making them ideal for photolithography. The global photonics market is expected to reach $1 trillion by 2025. This growth indicates the increasing reliance on quartz in optical systems, yet challenges remain in the consistency of quartz quality. Variations can impact performance, leading to potential setbacks in production schedules.
Moreover, quartz plates are used in laboratory instruments. Their thermal stability is crucial for precise measurements. Research shows that quartz is preferred in mass spectrometry and atomic absorption spectroscopy due to its reliability. However, manufacturers face hurdles in balancing cost and quality. The need for high-purity quartz is vital, yet sourcing it can be problematic, leading to potential delays in research and development.
| Industry | Application | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Electronics | Waveguide Windows | Used in communication devices to transmit light signals. |
| Optics | Lens Manufacturing | Quartz plates are used to create high-precision optical lenses. |
| Medical | Diagnostic Equipment | Utilized in devices like spectrophotometers for accurate measurements. |
| Aerospace | Sensor Windows | Quartz plates are used in sensors for their durability and optical clarity. |
| Semiconductors | Wafer Manufacturing | Quartz plates are used as substrates in the fabrication of semiconductor wafers. |
| Research | Laboratory Equipment | Quartz plates are critical in various experiments, especially in photonics. |
The manufacturing process of quartz plates is a blend of precision and technology. Quartz, a natural mineral, undergoes multiple transformations to become a usable product. Initially, raw quartz is extracted and crushed. The crushing results in small granules, ready for further processing. This stage is critical; it requires high-quality control to avoid impurities.
After crushing, the quartz is mixed with resins and other additives. This mixture is then subjected to a vacuum process. The vacuum removes air and bubbles, ensuring a smooth finish. It’s interesting to note that recent industry reports indicate that over 40% of quartz plate manufacturers have adopted state-of-the-art vacuum technology. This has enhanced product quality significantly.
The final step involves curing at high temperatures. This solidifies the mixture, creating a robust and durable plate. However, not all plates meet the stringent standards required for high-end applications. Faulty batches often arise due to inadequate initial material selection. A recent survey showed that around 15% of quartz plates produced globally exhibit defects. This highlights the importance of quality checks throughout the manufacturing journey.

Quartz plates are essential in various technological and scientific applications. They are widely used because of their unique properties. Quartz is durable and resistant to high temperatures. This makes it ideal for laboratory equipment and precision instruments. Researchers rely on quartz plates for experiments that require high purity and stability.
Benefits of quartz plates include their excellent optical clarity. They allow for precise measurements of light wavelengths. This is crucial in spectroscopy and other analytical techniques. Researchers can observe reactions without interference. Quartz plates also provide good thermal conductivity. This helps maintain consistent temperatures during experiments.
**Tip:** When selecting quartz plates, consider the thickness. Thicker plates can withstand higher pressures but may alter some measurements. Use different thicknesses for varied applications. Also, be sure to clean the plates properly before use. Residues can affect results and lead to inaccuracies. Always evaluate the results critically. Not everything might go as planned, and that's part of the process.