Quartz is one of the most abundant minerals on Earth. Its strength makes it a crucial material in various industries. To assess the "Strength of Quartz," accurate measurement techniques are vital. According to a recent report by the International Mineral Association, the global quartz market is predicted to grow by 6% annually, driven by its applications in electronics and construction.
Dr. Amelia Chen, an expert in mineral sciences, emphasizes, "Measuring the strength of quartz accurately is essential for ensuring its application in high-stress environments." This highlights the need for consistent methods to evaluate its durability.
Many existing methods can be unreliable. Some techniques rely heavily on subjective interpretations, leading to inconsistencies. Developers often face challenges in standardizing strength assessments for quartz. Clarifying these methods and improving measurement accuracy is imperative for advancing the industry.

Quartz is a fascinating mineral with unique physical properties. It is the second most abundant mineral in the Earth's crust. Quartz crystals come in many forms, often displaying beautiful colors and patterns. This variety makes them popular in various applications. They are essential in electronics and can also be found in jewelry.
Understanding quartz involves exploring its hardness. Quartz ranks a solid seven on the Mohs hardness scale. This characteristic makes it durable and resistant to scratching. However, even strong quartz can be fractured under extreme pressure. This imperfection can impact its usability. Therefore, careful handling is vital. It's easy to overlook such details when measuring strength.
Another interesting aspect is quartz's ability to resonate. When subjected to mechanical stress, it can generate electric energy. This property allows quartz to be used in timekeeping devices and sensors. But, measuring this effect accurately is challenging. Slight changes in temperature or pressure can alter results. Thus, precision is crucial. Whether you are measuring hardness or piezoelectric properties, focus on the details. Each small mistake can lead to significant misunderstandings.
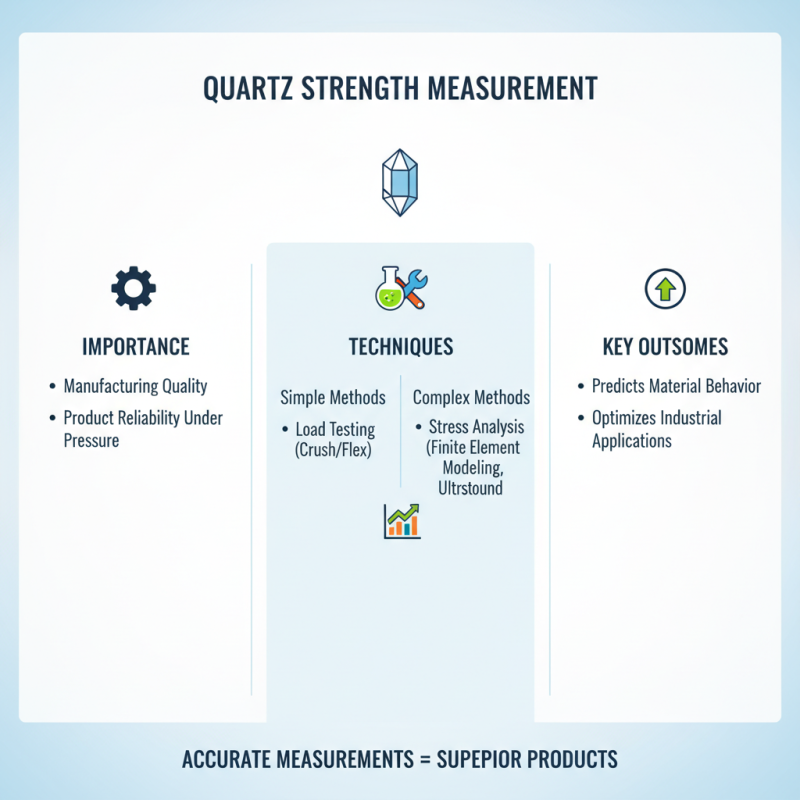
Measuring the strength of quartz is essential in various industries, especially in manufacturing. Techniques vary widely, from simple load testing to complex stress analysis methods. Accurate measurements can determine quartz’s behavior under pressure, influencing product quality.
The most common method involves the compressive strength test. Industry reports indicate that quartz can withstand pressures exceeding 100 MPa. This measurement often helps predict failure points. Another technique, the flexural strength test, assesses how quartz behaves under bending forces. Flexural strength typically hovers around 50-70 MPa in natural states, but variations depend on purity and grain size.
Microhardness tests also provide insights into quartz strength. Using tools like Vickers or Knoop, researchers gain granular data on crystal structures. Results show a range from 700 to 1200 HV. However, environmental factors can alter these figures. Many studies highlight discrepancies in measurements, raising questions on consistency. It’s crucial to reflect on methods and improve precision. Engaging in these tests allows for better understanding and innovative applications in the quartz industry.
Measuring the strength of quartz is crucial in several industries. Common tools include the Mohs hardness scale, which rates minerals. Quartz registers a hardness of 7. It's practical and widely accepted. However, this method does not provide detailed insights into fracture toughness or elasticity.
Another tool is the Rockwell hardness test. This method provides a quick measurement of hardness. It is efficient for bulk samples. However, its results can vary based on testing conditions. According to a study by the American Mineralogist, understanding quartz's mechanical properties needs a combination of methods.
Ultrasonic tests are also used. They measure wave velocity through quartz. This method gives information about density and elastic properties. While effective, it's sensitive to sample size and imperfections. There can be inconsistencies in real-world applications. A thorough approach is necessary to achieve reliable results.
Measuring the strength of quartz requires careful attention. Begin by selecting a representative sample. It should be clean and free of cracks. Consider the size and form of the quartz. Small pieces might yield variable results. Use a precision scale to weigh the sample accurately. Make sure to record the weight.
Next, apply a controlled force. A universal testing machine is ideal for this. Apply stress gradually to avoid sudden failure. Observe the sample as you increase the pressure. Take notes on any visible changes. This part can be quite challenging. Invisible fractures may form before any breakage occurs. Document these observations thoroughly.
Once you reach the breaking point, measure the force applied. This will give you a clear picture of quartz strength. Compare your results with standard values. If your results differ significantly, review your methodology. Consider if the equipment calibration was accurate. Reflect on the possible variations in sample preparation. These reflections can lead to better future measurements.
| Test Method | Description | Strength (MPa) | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Uniaxial Compression Test | Measures the compressive strength of quartz. | 120 - 150 | Commonly used in lab settings. |
| Flexural Strength Test | Measures resistance to bending. | 50 - 70 | Important for applications requiring bending. |
| Hardness Test (Mohs) | Rates quartz on the Mohs scale of hardness. | 7 | Indicates scratch resistance. |
| Tensile Strength Test | Measures the tensile strength of quartz materials. | 10 - 20 | Critical for composite materials. |
| Impact Test | Assesses the material's ability to withstand sudden forces. | Varies based on form | Useful for understanding durability. |
Measuring quartz strength requires careful analysis of the data collected. The process often involves testing different samples under controlled conditions. Accurate readings depend on various factors like temperature and pressure. Each test must be meticulously documented. Small variations can lead to misleading results.
Interpreting the results can be tricky. Not all tests yield clear outcomes. Some samples may show unexpected weaknesses. It’s vital to analyze these anomalies. Understanding the environment in which the quartz formed can provide insight. Geological factors often influence strength readings.
Data analysis involves comparing results from multiple tests. Trends must be identified, but not all will be consistent. Some samples will challenge initial assumptions. It's essential to remain open-minded. Anomalies can reveal new information about quartz properties. Continuous reflection on the testing process can enhance accuracy.
This chart illustrates the measured strength of quartz samples across various conditions. The strength is measured in megapascals (MPa) for each sample condition, showcasing how quartz performs under different stress conditions.