In the glass manufacturing industry, silica plays a vital role. Experts emphasize its significance. Dr. Emily Carter, a leading authority on glass materials, once stated, "The quality of silica directly influences glass durability." This highlights the importance of using silica in glass effectively.
Silica in glass is not just a passive ingredient. It serves as a fundamental component that determines clarity and strength. However, manufacturers must reflect on their processes. Not every method maximizes silica’s potential. Waste and inefficiencies often arise during production, leading to increased costs.
Exploring innovative approaches can enhance silica use in glass. For example, sourcing silica from sustainable deposits can reduce environmental impact. Yet, challenges persist in ensuring consistency. As the industry grows, outdated practices must be reconsidered. The future relies on adaptable strategies that improve the use of silica in glass.
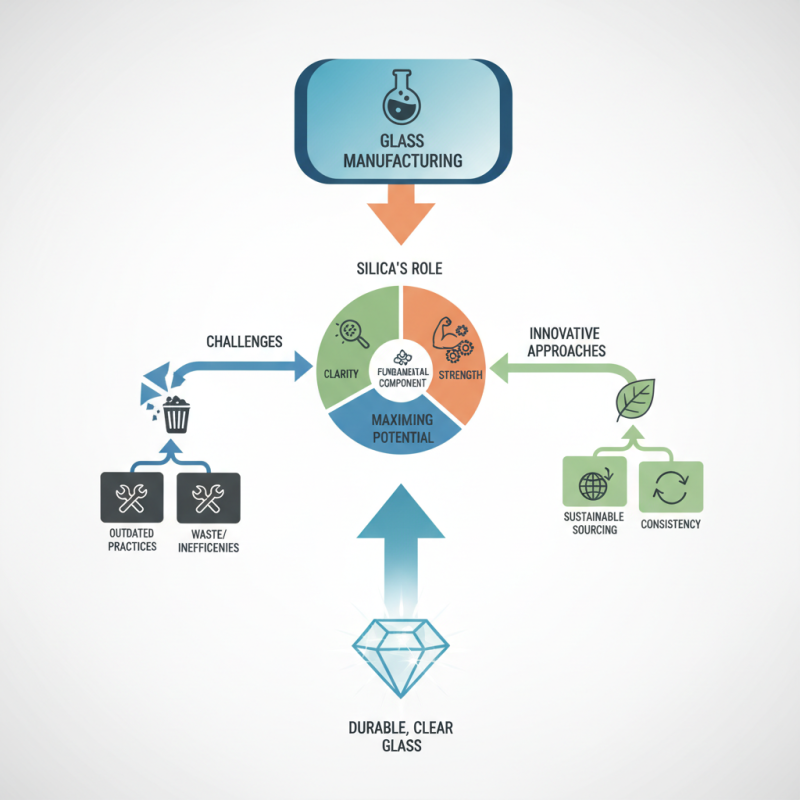
Silica plays a critical role in glass manufacturing. It serves as the primary raw material, providing the fundamental structure of glass. Without silica, glass would lack durability and clarity. The purity of silica significantly affects the quality of the final product. Impurities can lead to defects or undesirable colors in the glass.
Effective utilization of silica requires careful consideration. The grain size and type of silica matter greatly. Coarse grains may not melt uniformly, resulting in inconsistent glass quality. Fine particles can improve melting efficiency but may result in excessive fining. Finding the right balance can be challenging.
Monitoring silica sourcing is also key. Variations in silica quality from different suppliers can impact production. Regular testing is essential to ensure consistency. Sometimes, even small changes can lead to larger production issues. Proper training for staff is equally important. Ensuring everyone understands silica's role can improve overall operations. Companies need to reflect on their processes continually to enhance efficiency.
Silica is crucial in glass manufacturing. Various types of silica impact the efficiency and quality of glass. The main types include quartz, silica sand, and fused silica. Each serves specific roles and contributes differently to the final product.
Quartz is the most common form. It provides strength and clarity to glass. Silica sand, widely used in bulk, influences viscosity and melting points. A recent study noted that up to 70% of glass production relies on silica sand, revealing its importance. Fused silica, although more expensive, offers thermal stability and lightweight properties.
Tips: Always source high-purity silica for better glass yield. Low-quality silica can cause defects and increase production costs. Monitor particle size distribution closely. Variability here can affect melting behavior and final glass properties. When selecting silica, consider local availability to reduce transportation costs. Remember, not all silica is created equal—different applications require tailored solutions.
Silica, primarily composed of silicon dioxide, is critical in glass manufacturing. Its unique properties significantly influence the quality of the final product. High-purity silica, with less than 0.1% contaminants, yields clearer glass. According to the Glass Technical Advisory Group, impurities can lead to discoloration and reduced clarity.
The particle size of silica also matters. Finer particles enhance melting efficiency but may require careful handling to avoid dust. Research indicates that a well-controlled particle size distribution can optimize melting rates and energy consumption. Nevertheless, achieving the perfect blend is a challenge. Glass manufacturers often grapple with balancing silica's properties against production costs and energy efficiency.
Viscosity plays a vital role as well. Silica lowers the viscosity of molten glass, affecting the ease of shaping and forming. If viscosity is too high, production slows, impacting productivity. A study from the American Ceramic Society suggests that maintaining an optimal silica concentration helps minimize viscosity issues during hot working. Striking this balance remains an area for continuous improvement in the industry.
| Property | Description | Importance in Glass Manufacturing |
|---|---|---|
| Purity | High-quality silica should have a purity of over 99% | Ensures clarity and reduces defects in glass products |
| Particle Size | Fine and uniform particle size is essential | Affects melting characteristics and final glass texture |
| Moisture Content | Minimal moisture content is required | Prevents clumping and ensures uniform melting |
| Color | Colorless or very light tinted silica is preferred | Affects the aesthetic quality of glass |
| Thermal Stability | Must withstand high temperatures during production | Ensures durability and integrity of the final product |

Incorporating silica in glass manufacturing is essential for achieving the desired quality and properties. Efficient methods can significantly enhance the melting process. One effective approach is to maintain the proper temperature. Silica requires high heat to melt effectively. Ensure that your furnace consistently reaches optimal temperatures for better results.
Tips: Regularly calibrate temperature sensors. This ensures accuracy and helps in maintaining consistent melting conditions.
Another method involves optimizing the particle size of silica. Smaller particles melt more easily than larger ones, leading to a smoother glass finish. Consider sourcing finer silica sand or grinding larger particles to expedite the melting process.
Tips: Use a sieving method to separate different particle sizes. This can improve the uniformity of your silica feed.
It’s crucial to monitor the silica content in the mixture. Too much can lead to a brittle glass, while too little may produce a weak structure. Striking the right balance requires careful measurement and adjustment throughout production.
Tips: Document each batch’s composition. This will aid in refining the process over time and enhance overall quality.

Sustainability in silica sourcing for glass manufacturing is critical. The glass industry consumes about 50 million tons of silica sand annually. This demand raises concerns about environmental impact. Silica extraction can damage ecosystems and deplete natural resources. Responsible sourcing practices must be adopted to mitigate these effects.
Many companies are now prioritizing sustainability. Using recycled glass, or cullet, can significantly reduce silica needs. Studies indicate that incorporating 30% cullet into glass production can lower energy consumption by up to 20%. This is a notable strategy for minimizing the carbon footprint. However, the availability of cullet varies regionally, making it essential to create robust supply chains.
Another key aspect is sourcing silica from local suppliers. Local sourcing not only reduces transportation emissions but also supports local economies. Yet, it's important to assess the long-term sustainability of silica mines. Many operations lack transparency, leading to potential resource mismanagement. Industries must advocate for ethical practices in silica sourcing to protect resources for the future.