When it comes to selecting the perfect Quartz Plate for a specific application, it is essential to consider various factors that can influence performance and efficiency. Quartz plates are highly valued in numerous fields, including electronics, optics, and laboratory settings, due to their exceptional properties such as high thermal stability, chemical resistance, and optical clarity. With the right knowledge and understanding of your unique requirements, you can make an informed decision that aligns with your operational needs.
In this guide, we will explore key considerations for choosing the best Quartz Plate suitable for your applications. Whether you are looking for plates that can withstand high temperatures or those that offer superior transmission in ultraviolet and visible light, understanding your specific needs will help streamline the selection process. Additionally, we will delve into various attributes such as thickness, surface quality, and compatibility with other materials, empowering you to optimize your use of quartz plates effectively. Ultimately, the right choice will enhance your project's success and functionality.

When it comes to selecting the right quartz plate for your specific needs, understanding the difference between standard and custom options is crucial. Standard quartz plates are mass-produced and readily available, making them a cost-effective choice for many applications. They come in various sizes and thicknesses, catering to general requirements in industries such as electronics, optics, and scientific research. These pre-made options are typically designed to meet typical specifications and are often chosen for their reliability and availability.
On the other hand, custom quartz plates offer flexibility and specificity for unique applications. These plates can be tailored in terms of dimensions, shapes, and optical properties, thereby addressing specialized requirements that standard plates may not fulfill. Industries such as semiconductor manufacturing and photonics often demand custom solutions to ensure optimal performance in their specific environments. By opting for custom quartz plates, you can achieve precise characteristics, such as enhanced durability or increased thermal resistance, which are vital for successfully executing demanding tasks. Making an informed choice between standard and custom options allows you to align your quartz plate selection with your application needs effectively.
This chart compares the percentage usage of standard versus custom quartz plates in various applications, highlighting that standard quartz plates are more widely used, accounting for 65% of applications, while custom options make up 35%.
When selecting a quartz plate, understanding its key properties is crucial to ensure it meets your specific needs and applications. One of the primary attributes of quartz plates is their hardness. Quartz is known for its durability, ranking high on the Mohs scale, making it resistant to scratches and wear. This hardness not only extends the lifespan of the material but also makes it suitable for applications in environments where impact and abrasion are common, such as in laboratory equipment or industrial machinery.
Another essential property to consider is chemical resistance. Quartz plates exhibit excellent resistance to a wide range of chemicals, making them ideal for use in laboratories and industries where exposure to corrosive substances is prevalent. Their non-reactive nature ensures that they maintain integrity and do not contaminate samples or materials. This is particularly beneficial in chemical processing or pharmaceutical applications where purity and safety are paramount.
Thermal stability is also critical when choosing a quartz plate. These plates can withstand high temperatures without deforming or degrading, making them suitable for applications in both high-temperature environments and processes that involve sudden temperature changes. This thermal resilience allows quartz plates to be used in various industrial settings, including oven components and heat exchangers, where reliability and performance are necessary under extreme conditions.
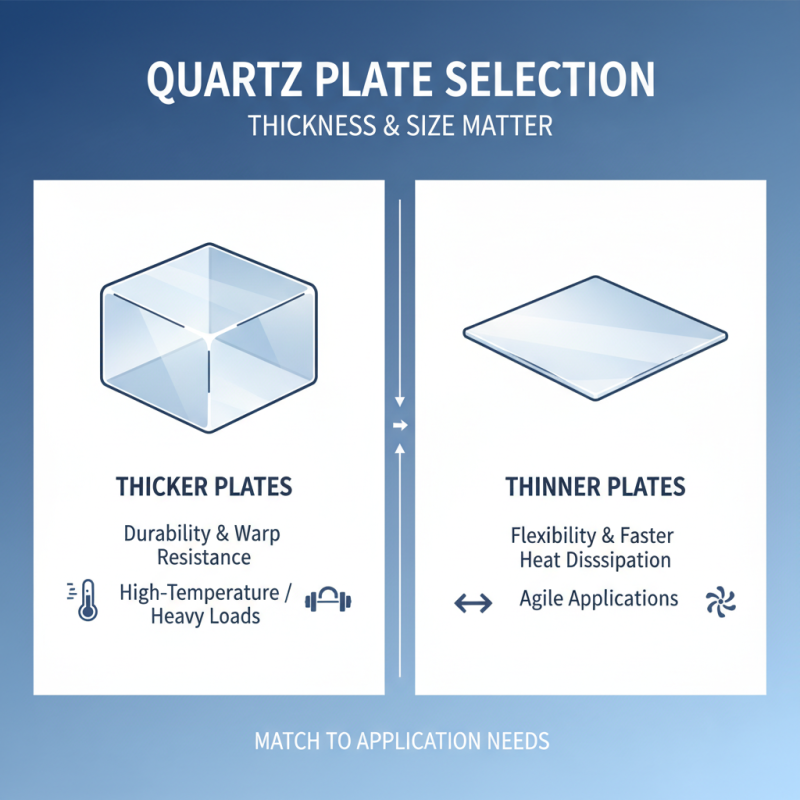
When selecting a quartz plate for specific needs, assessing its thickness and size is essential, as these dimensions significantly influence performance. Thicker plates often offer improved durability and resistance to warping, making them ideal for high-temperature applications or environments where heavy weights are applied. On the other hand, thinner plates can be more suitable for applications requiring heightened flexibility or faster heat dissipation. It's crucial to evaluate the specific demands of your application to determine the optimal thickness.
Size plays a pivotal role in functionality. A quartz plate that is too large may be cumbersome, affecting ease of handling and installation. Conversely, an undersized plate might not accommodate the necessary equipment, leading to inefficiencies. When choosing the right dimensions, consider the area you will be working in and any equipment specifications that dictate the size requirements.
**Tips:** Always measure your workspace and equipment accurately before purchasing. This will help you avoid the pitfalls of selecting an ill-fitting plate. Additionally, consulting with professionals who have experience in quartz applications can provide valuable insights and ensure you make an informed choice that enhances your operational efficiency.
When considering quartz plates for specific applications, understanding the manufacturing processes behind fused quartz and engineered quartz plates is crucial. Fused quartz is created by melting high-purity silica at extremely high temperatures, producing a highly transparent and durable material. This process ensures that the resultant plates have exceptional thermal resistance and minimal impurities, making them ideal for high-temperature applications such as semiconductor production and laboratory settings.
On the other hand, engineered quartz plates are made by combining natural quartz crystals with resins and polymers. This method allows for greater versatility in design and performance characteristics. Engineered quartz can be produced in a variety of colors and textures, making it suitable for aesthetic applications such as countertops and decorative elements. While generally less thermally resistant than fused quartz, engineered quartz still offers reliable durability and can withstand moderate heat.
In evaluating which type of quartz plate best meets your needs, consider factors such as thermal stability, transparency, and aesthetic flexibility. Each manufacturing process offers distinct advantages that align with different application requirements, ensuring that users can choose a quartz plate that perfectly suits their specific use cases.
| Property | Fused Quartz | Engineered Quartz |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | 99.99% SiO2 | Silica + Resin |
| Durability | High thermal resistance | Good impact resistance |
| Thermal Expansion | Low | Moderate |
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent | Good, but resin can degrade |
| Applications | High-temperature applications | Countertops, vanity tops |
| Cost | Higher | Lower |
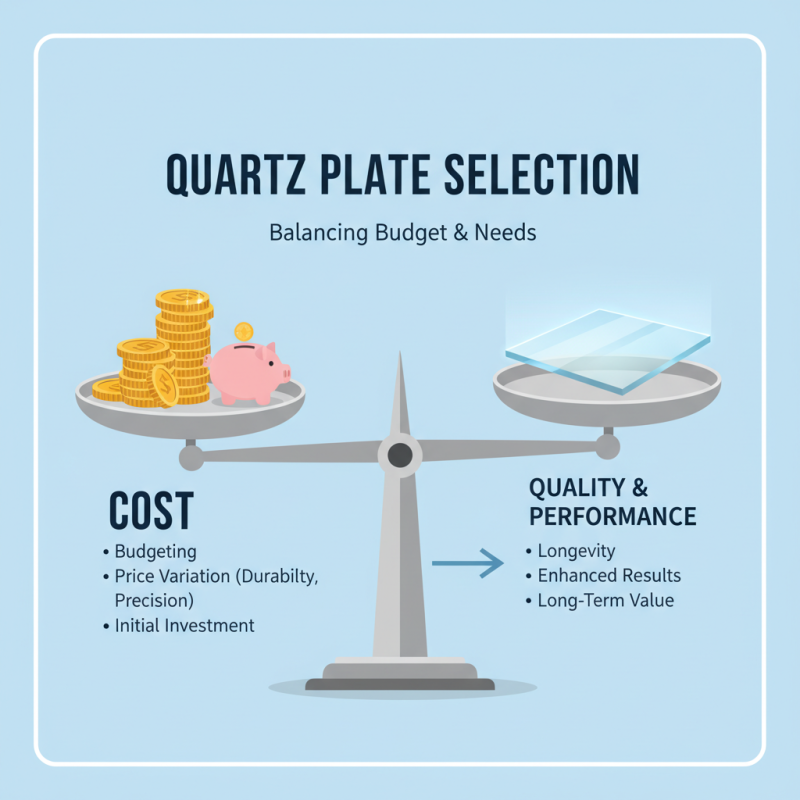
When selecting the best quartz plate for your specific needs, cost considerations play a crucial role in balancing your budget with the quality and performance you require. High-quality quartz plates can vary significantly in price, often influenced by their durability, precision, and the complexity of manufacturing processes. Deciding on your budget is vital, but it is equally important to understand what you are paying for. Investing in a more expensive plate may yield better performance and longevity, making it a wise choice in the long run.
Tips: Before you settle on a price point, consider the specific applications of the quartz plate. For instance, if you intend to use the plate for high-temperature applications, a slightly higher investment may be necessary to ensure durability and reliability. Additionally, always consider the manufacturer's reputation for quality, as a well-regarded source may offer better value even at a higher price.
Balancing budget with quality also involves reviewing long-term costs. A cheaper quartz plate may save you money upfront, but if it needs to be replaced frequently or doesn’t perform well, those savings can quickly diminish. Evaluate your requirements carefully, taking into account not just the initial cost but the lifetime value and performance of the quartz plate, ensuring you make a choice that meets both your budget and operational needs effectively.